Tooth Infection Antibiotics Explained for Dental Patients
Tooth pain can quickly become upsetting, especially when it comes with pain and swelling that does not improve. Many patients search for antibiotics for tooth infection because they want fast relief and reassurance. While antibiotics can help in certain situations, they are not always the first or only step in treating dental infections.
This guide explains tooth infection antibiotics in a clear, patient-friendly way. You’ll learn what causes dental infections, common symptoms, when a dentist may prescribe antibiotics, and why professional dental care is still essential. If you are dealing with tooth pain or think you may have an infected tooth, understanding your options can help you feel more confident and prepared.
What Is a Tooth Infection?
A tooth infection develops when bacteria enter the tooth or nearby gums and begin to spread. This often happens when tooth decay, cracks, or gum disease allow bacteria to reach deeper areas of the tooth or the surrounding tissue.
One of the most common dental infections is a tooth abscess. An abscess is a pocket of pus caused by bacteria that forms near the root of an infected tooth or along the gum line. Because an abscess is a pocket of pus, it often causes pressure, pain, and visible swelling. If left untreated, a dental infection can spread and affect nearby areas.
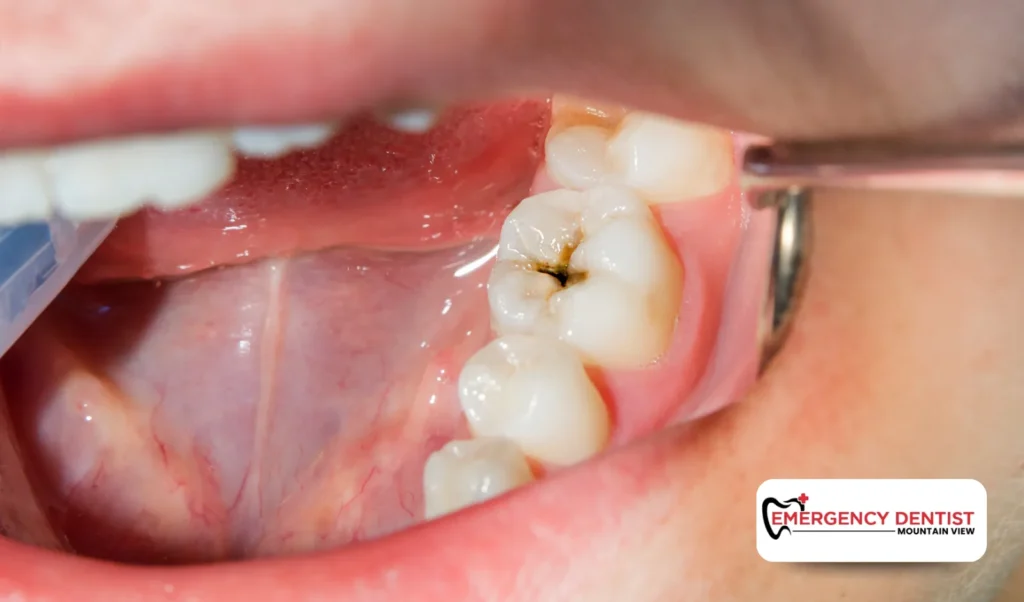
Common Causes of Dental Infections
Dental infections often start with everyday dental problems, including:
- Untreated cavities
- Cracks or chips that expose the inner tooth
- Gum disease that allows bacteria below the gum line
- Delayed or incomplete dental work
- Poor oral hygiene habits over time
When bacteria reach the inner tooth, the risk of infection increases. Without proper treatment, dental infections can lead to ongoing tooth pain and damage to surrounding tissue.
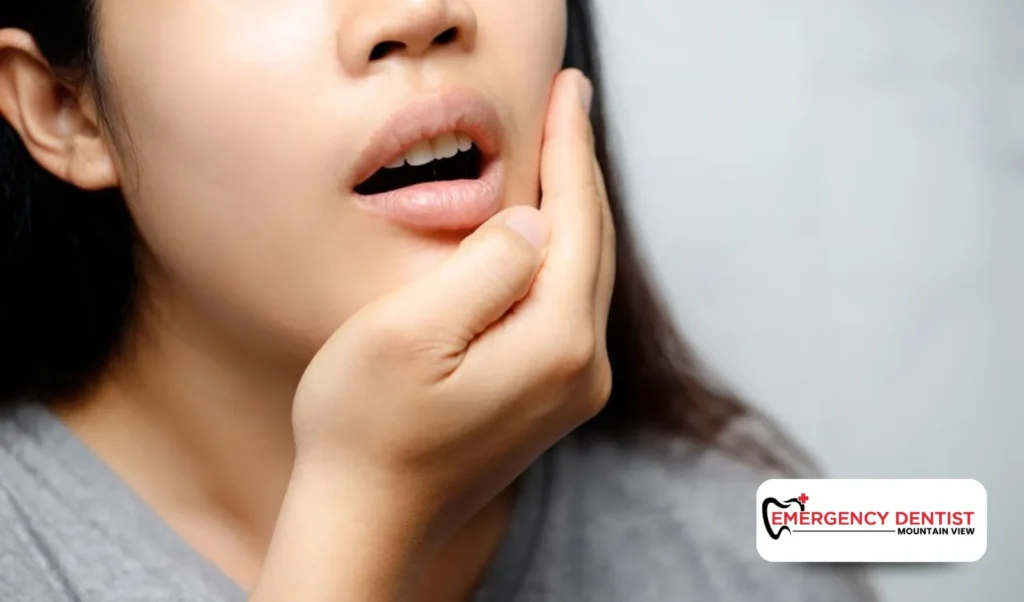

Symptoms That May Signal a Tooth Infection
Symptoms can vary, but many patients experience:
- Persistent tooth pain
- Pain and swelling in the gums, jaw, or face
- Sensitivity when chewing or biting
- A bad taste in the mouth
- Tenderness near the infected tooth
If the infection has spread, symptoms may become more intense or affect nearby areas. Any tooth pain that does not improve should be evaluated by a dentist. Many dental infections are manageable with timely care and the right treatment plan.
How Antibiotics Are Used for Tooth Infections
Patients often ask about the best antibiotic for tooth infection, but antibiotics alone do not cure dental infections. Dentists may prescribe antibiotics when there are signs the infection has spread, when pain and swelling are present, or when surrounding tissue is affected.
A commonly prescribed antibiotic may help control bacteria while dental procedures are planned or completed. If a patient is allergic to penicillin, the dentist can choose alternative medications that are appropriate and safe.
An antibiotic for tooth infection is meant to support treatment, not replace it. The infected tooth still needs professional care to fully treat tooth infections and lower the chance of recurrence.
Why Dental Procedures Are Still Necessary
Antibiotics cannot remove decay or repair damaged teeth. Dental procedures are usually required to fully resolve dental infections.
Depending on the situation, treatment may involve fillings, drainage, or a root canal. A root canal removes infected tissue from inside the tooth, helping protect the surrounding tissue and preserve as much of the natural tooth as possible.
Without proper dental treatment, symptoms may return even if antibiotics temporarily reduce discomfort.
Important Things to Know About Antibiotics
If antibiotics are part of your treatment plan, keep these points in mind:
- Always finish the full course, even if you feel better
- Be aware of possible side effects, such as stomach upset
- Tell your dentist about medication allergies or past reactions
- Antibiotics manage bacteria but do not fix tooth damage
Used correctly, antibiotics can safely support dental care as part of a complete treatment approach.
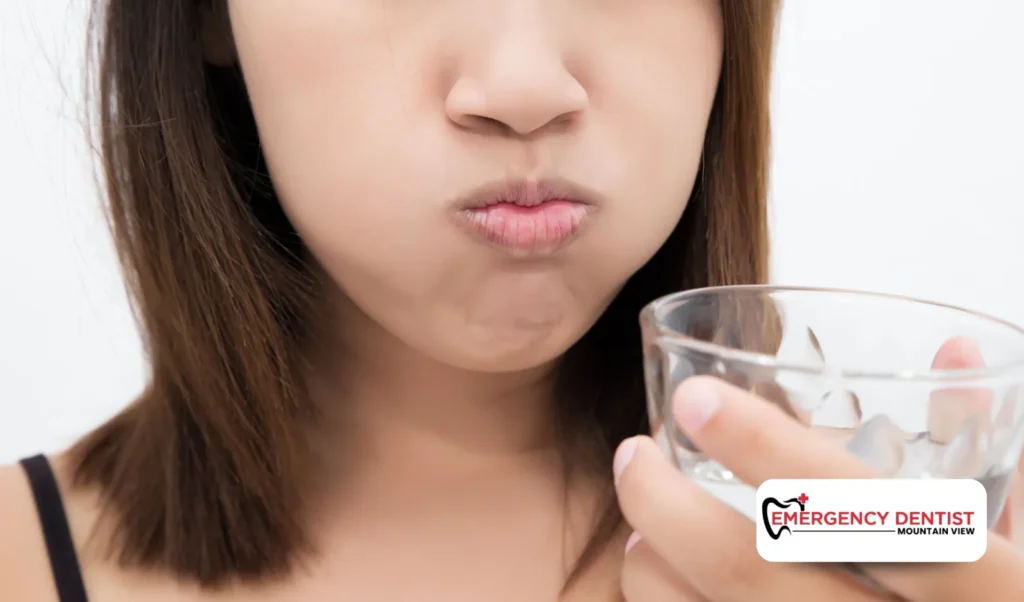

What Patients Can Do at Home
While waiting for professional care, gentle steps may help reduce discomfort:
- Rinse with warm salt water
- Avoid chewing on the affected side
- Maintain good oral hygiene with gentle brushing
- Stay hydrated and avoid very hot or sugary foods
These steps do not replace dental care, but they may help you stay more comfortable.
When to Call a Dentist Right Away
Contact a dentist promptly if you notice:
- Tooth pain lasting more than a day
- Swelling in the gums, face, or jaw
- Signs of a tooth abscess
- Pain that interferes with eating or sleeping
- Symptoms that continue despite home care
Prompt treatment helps prevent dental infections from worsening.
Conclusion
Searching for tooth infection antibiotics often means a deeper dental issue needs attention. While antibiotics can play a helpful role, proper evaluation and dental care are essential for protecting your smile and preventing future problems.
If you are experiencing tooth pain, discomfort and swelling, or signs of an infected tooth, early care can reduce discomfort and lower the risk of complications.
Get Help for Tooth Infection Symptoms in Mountain View
If you are dealing with ongoing tooth pain or concerns about dental infections, you don’t have to handle it alone. Professional dental care can help identify the cause and guide you toward the right treatment options.
The compassionate team at Emergency Dentist in Mountain View provides prompt, supportive care for urgent dental concerns. Whether symptoms start suddenly or worsen over time, reaching out sooner can help protect your oral health and bring peace of mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do antibiotics for tooth infection cure the infection completely?
Antibiotics for tooth infection can help control bacteria and reduce pain and swelling, but they do not fix the underlying dental problem. Dental care is still needed to treat the infected tooth and prevent the infection from returning.
When does a dentist prescribe an antibiotic for tooth infection?
A dentist may prescribe antibiotics if the infection has spread, is causing noticeable swelling, or is affecting surrounding tissue. Tooth infection antibiotics are usually used alongside dental procedures, not as a replacement for treatment.
What is a tooth abscess and why does it need treatment?
A tooth abscess is a dental infection where an abscess is a pocket of pus caused by bacteria. It can lead to pressure, pain, and swelling and should be evaluated promptly to avoid further complications.
What should I do if I am allergic to penicillin?
If you are allergic to penicillin, tell your dentist before starting treatment. There are other commonly prescribed antibiotic options that may be used safely to help manage dental infections.
Should I still see a dentist if antibiotics reduce my tooth pain?
Yes. Even if tooth pain improves, dental treatment such as a filling or root canal may still be necessary. Without proper dental care, the infection may return or worsen over time.




